Port Mirroring
Port mirroring is a powerful feature that allows you to copy packets traversing a physical switch port and send them to another port for analysis. This is crucial for monitoring and troubleshooting network traffic without disrupting normal operations.
Configuring Port Mirroring
In DENT, port mirroring is configured using the tc command with the matchall filter and the mirred egress mirror action. Refer to tc-mirred(8) and tc-matchall(8) for detailed information on these commands.
To configure port mirroring from one port to another, use the following commands:
tc qdisc add dev <PORT> clsact
tc filter add dev <PORT> (ingress|egress) matchall skip_sw action mirred egress mirror dev <TO-PORT>
<PORT>: The port from which traffic will be mirrored.<TO-PORT>: The port that will receive the mirrored traffic.
In this context, ingress refers to the incoming direction of the original traffic, while egress is the direction for the mirrored traffic queue. The skip_sw flag ensures that the mirroring occurs only in hardware, bypassing the kernel.
Mirroring ingress and egress traffic
Ingress Traffic Mirroring
To mirror incoming traffic from swp21 to the analyzer port swp22:
# Mirror ingress traffic from swp21 to analyzer port swp22
tc filter add dev swp21 ingress matchall skip_sw action mirred egress mirror dev swp22
Output:
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0 handle 0x1
action order 1: mirred (Egress Mirror to device swp22) stolen
index 1 ref 1 bind 1
Egress Traffic Mirroring
To mirror outgoing traffic from swp23 to the analyzer port swp24:
# Mirror egress traffic from swp23 to analyzer port swp24
tc filter add dev swp23 egress matchall skip_sw action mirred egress mirror dev swp24
Output:
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0 handle 0x1
action order 1: mirred (Egress Mirror to device swp24) stolen
index 1 ref 1 bind 1
Mirroring Traffic from Multiple Ports
To mirror traffic from multiple ports, you can use the ingress_block and egress_block configurations:
Mirroring ingress traffic from multiple ports:
tc qdisc add dev swp25 ingress_block 1 clsact
tc qdisc add dev swp26 ingress_block 1 clsact
tc filter add block 1 ingress matchall skip_sw action mirred egress mirror dev swp27
Output:
qdisc clsact 8001: dev swp25 root refcnt 2
qdisc clsact 8001: dev swp26 root refcnt 2
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0 handle 0x1
action order 1: mirred (Egress Mirror to device swp27) stolen
index 1 ref 1 bind 1
Mirroring egress traffic from multiple ports:
tc qdisc add dev swp28 egress_block 2 clsact
tc qdisc add dev swp29 egress_block 2 clsact
tc filter add block 2 egress matchall skip_sw action mirred egress mirror dev swp30
Output:
qdisc clsact 8001: dev swp28 root refcnt 2
qdisc clsact 8001: dev swp29 root refcnt 2
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0 handle 0x1
action order 1: mirred (Egress Mirror to device swp30) stolen
index 1 ref 1 bind 1
Example Configuration
To verify the configuration, perform a simple ping test from VPC1 to VPC2 and check if the mirrored traffic appears on the analyzer port.
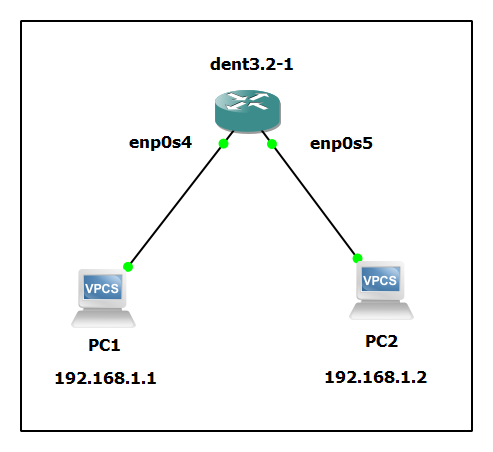
Set up port mirroring from enp0s4 to enp0s5:
tc qdisc add dev enp0s4 clsact
tc filter add dev enp0s4 ingress matchall skip_sw action mirred egress mirror dev enp0s5
Verify the configuration:
tc filter show dev enp0s4 ingress
Output:
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0
filter parent ffff: protocol all pref 49152 matchall chain 0 handle 0x1
action order 1: mirred (Egress Mirror to device enp0s5) stolen
index 1 ref 1 bind 1
Ping from VPC1 connected to enp0s4 to VPC2 with the IP address 192.168.1.2:
ping 192.168.1.2
Output:
PING 192.168.1.2 (192.168.1.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.123 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.112 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.110 ms
Check the mirrored traffic on the analyzer port enp0s5:
Use a packet analyzer tool like tcpdump on enp0s5 to verify the mirrored traffic:
tcpdump -i enp0s5
Output:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on enp0s5, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
10:00:00.000000 IP 192.168.1.1 > 192.168.1.2: ICMP echo request, id 1, seq 1, length 64
10:00:00.000123 IP 192.168.1.2 > 192.168.1.1: ICMP echo reply, id 1, seq 1, length 64
10:00:01.000000 IP 192.168.1.1 > 192.168.1.2: ICMP echo request, id 1, seq 2, length 64
This verifies that the port mirroring is configured correctly and the mirrored traffic is being captured on the analyzer port enp0s5.
Special Considerations
- Mirrored packets bypass eVLAN/VLAN and Spanning Tree filtering on the analyzer port. This allows mirroring from a port in one VLAN/Bridge to a port in a different VLAN/Bridge.
- The
skip_swflag ensures that mirroring occurs in the hardware, providing better performance and lower latency.
Limitations
- The number of rules is limited by the supported port mirror combinations.
- A source port cannot be bound to multiple analyzer ports.
- Filter rules must have a higher priority than the lowest priority flower rules. The
matchallfilter takes precedence over flower ACL rules. - The number of filters does not affect the maximum ACL rule count.
- A source port can also function as an analyzer port.
- Drop counter statistics are not supported.