IGMP Snooping
Introduction
In this guide, we will quickly explain what IGMP Snooping is and give an example implementing it.
IGMP snooping is a network switch feature that enhances the efficiency of the multicast traffic delivery. Since IGMP Snooping occurs at Layer 2 it will use the bridge driver for coordinating multicast transmissions. Bridges, by default, may flood traffic to all enslaved ports.
IGMP Snooping makes it so that Multicast transmissions will only go down ports where there are devices a part of a given multicast group.
Multicast Database (MDB)
The Multicast Database (MDB) contains all known L2 multicast group addresses (mac address) on a link. The MDB is how the Bridge driver keeps track of all registered multicast groups and, as such, is essential for IGMP Snooping.
Creating a static MDB Group
First, create a bridge with
$ ip link add name br0 type bridge
To create a static MDB group (or add a port to an already existing group) on a bridge, enter the following command:
$ bridge mdb add dev ${DEV} port ${PORT} grp ${GROUP} ${<permanent|temp>} ${vid}
Detailed Descriptions:
| Configure | Description |
|---|---|
| DEV | The interface where this group address is associated |
| PORT | The port whose link is known to have members of the multicast group |
| GROUP | The multicast group address whose members reside on the link connected to the port |
| permanent | Indicate that the MDB entry is permanent |
| temp | Indicates that the MDB entry is temporary (default) |
| vid | The VLAN ID for the multicast group |
Ex.
Using a MAC address:
$ bridge mdb add dev br0 port veth1 grp 01:00:00:00:00:04 permanent vid 1
Using an IPV4 address:
$ bridge mdb add dev br0 port veth1 grp 239.255.255.255 permanent vid 1
Deleting a single MDB Group
To delete a group or a single port from a group, enter the following command:
$ bridge mdb delete dev ${DEV} port ${PORT} grp ${GROUP} ${<permanent|temp>}
Ex.
$ bridge mdb delete dev br0 port veth1 grp 239.255.255.255 permanent vid 1
NOTE: Deleting a bridge will automatically clear all MDB groups associated with the Bridge
Viewing an MDB Table
To view an MDB table, enter the following command:
$ bridge mdb show dev ${Bridge Name}
Additional filters can also be included to alter the output of this command:
-
To show the ‘time to live’ of any shown MDB group (time till expiration), use
-d -
To only show multicast router ports, use
-s
Ex.
root@localhost:~# bridge mdb show dev br0
dev br0 port enp0s7 grp ff02::1:ff2f:1 temp
dev br0 port enp0s5 grp ff02::1:ff6c:1 temp
dev br0 port enp0s6 grp ff02::1:ff8c:1 temp
dev br0 port enp0s4 grp ff02::1:ffb8:2 temp
dev br0 port br0 grp ff02::1:ff54:1 temp
dev br0 port br0 grp ff02::6a temp
Enabling IGMP Snooping
In order to use IGMP Snooping, mcast_snooping must be enabled on the bridge. mcast_snooping enables the management of multicast traffic. It is responsible for the multicast traffic being forwarded intelligently to only those ports where the interested hosts are connected.
By default, multicast snooping is disabled and mcast_snooping will be 0.
To enable IGMP snooping on a bridge, set mcast_snooping to 1:
Ex.
$ ip link set dev ${Bridge Name} type bridge mcast_snooping 1
Multicast Querying
In addition to enabling mcast_snooping, multicast querying is also needed for IGMP Snooping. When the mcast_querier flag is enabled, a bridge can act as the source for sending out multicast query messages and managing multicast group memberships within a network segment.
By default, multicast queries by a bridge are disabled and mcast_querier will be 0.
To enable multicast querying on a bridge, set mcast_querier to 1.
Ex.
$ ip link set dev ${Bridge Name} type bridge `mcast_querier` 1
Additional Configurations
Multicast Routers
Another tool for network administrators is the mcast_router attribute.
There are three settings for the multicast_router attribute:
0The bridge device will not forward any multicast traffic to its ports.1The bridge device will act as a multicast router, forwarding multicast traffic according to the multicast forwarding database.2The bridge device will forward all multicast traffic to all of its ports, regardless of the multicast forwarding database.
By default, mcast_router will be 1.
Setting this flag to 2 is useful in cases where the multicast router is not present, or when there is a need for forwarding both known and unknown IP multicast to a another router.
Ex.
$ ip link set dev ${Bridge Name} type bridge `mcast_router` 2
Multicast Flooding
Multicast flooding can also be changed using the mcast_flood attribute. This attribute controls whether multicast traffic, for which there is no MDB entry, will be flooded toward a given port.
There are two settings for the mcsat_flood attribute:
onFlood multicast traffic on ports where there is no MDB entryoffMulticast traffic is NOT sent down ports where there is no MDB entry
By default, mcast_flood will be on.
Ex.
$ bridge link set dev ${Port Name} mcast_flood off
IGMP Version
The IGMP version can also be changed using the mcast_igmp_version attribute.
There are two settings for the mcast_igmp_version attribute:
2Sets the IGMP version to IGMPv23Sets the IGMP version to IGMPv3
By default, mcast_igmp_version will be 2.
Ex.
$ ip link set dev br0 type bridge mcast_igmp_version 3
Example Configuration
Consider the following topology:
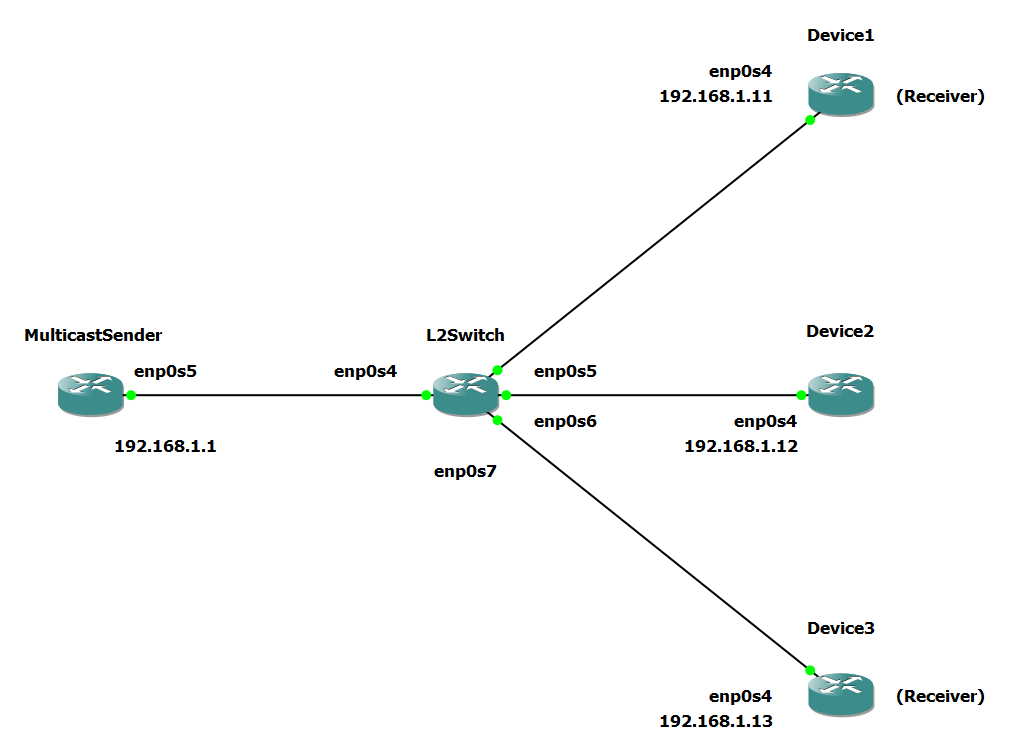
In this example, the MulticastSender will send packets to a multicast group IP address that Device1 and Device3 are a part of. The multicast group IP address will be 224.0.55.55, and the L2Switch will implement IGMP Snooping by querying and appropriately forwarding the packets to only Device1 and Device3.
We will use the iperf utility to generate the multicast traffic.
If the iperf utility is not already installed on the multicast sender and receiving devices:
Do not forget to use $ apt-get update to fetch the latest version of your package lists. Follow this with the command $ apt-get upgrade to first review the changes in the latest versions and then replace the old packages by installing the new ones.
Install the iperf utility with: $ apt-get install iperf
Configure the MulticastSender
On the MulticastSender, attach an IP address to the enp0s4 interface with the following:
$ ip address add 192.168.1.1 dev enp0s5
Do not forget to bring the interface up with
$ ip link set enp0s5 up
Finally, add the default route to know where to send multicast generated packets:
$ ip route add default dev enp0s5
Configure the End Devices
Bring the interfaces of all the end devices up with:
$ ip link set enp0s4 up
To have only Device1 and Device3 join a group multicast address use the following command on them:
$ ip address add 224.0.55.55 dev enp0s4
NOTE: End Devices can be added dynamically to an MDB table by including the keyword autojoin upon the addition of the IP address. In this example it is not needed as we will add the entry to the MDB table statically, but it is another useful feature for network administrators.
Ex.
$ ip address add 224.0.55.55 dev enp0s4 autojoin
Configure IGMP Snooping on the L2Switch
First, create a bridge on the L2 Switch running DENT to connect all interfaces on the LAN. Use the following to do so…
L2Switch:
$ ip link add name br0 type bridge
$ ip link set dev enp0s4 master br0
$ ip link set dev enp0s5 master br0
$ ip link set dev enp0s6 master br0
$ ip link set dev enp0s7 master br0
After the bridge is created, bring all interfaces up with the following:
$ ip link set dev enp0s4 up
$ ip link set dev enp0s5 up
$ ip link set dev enp0s6 up
$ ip link set dev enp0s7 up
$ ip link set dev br0 up
The MulticastSender can now reach all Devices. However, since IGMP Snooping is not configured, multicast traffic will be flooded on all ports, and all Devices will receive the multicast traffic.
To limit the ports that receive multicast traffic to only those a part of the group enable mcast_snooping and mcast_querrying on the switch with the following:
$ ip link set dev br0 type bridge mcast_snooping 1
$ ip link set dev br0 type bridge mcast_querier 1
Now, update the MDB table by adding the interfaces that are a part of the multicast group. In our example, the receiver devices are Device1 on interface enp0s5 and Device3 on interface enp0s7.
Add these two entries to the MDB table with the following:
$ bridge mdb add dev br0 port enp0s5 grp 224.0.55.55 permanent
$ bridge mdb add dev br0 port enp0s7 grp 224.0.55.55 permanent
Multicast traffic will now only be sent to Device1 and Device3.
To test the configuration was successful, we will use the iperf utility to generate multicast traffic from the MulticastSender:
MulticastSender:
root@localhost:~# iperf -c 224.0.55.55 -u -T 32 -t 3 -i 1
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 224.0.55.55, UDP port 5001
Sending 1470 byte datagrams, IPG target: 11215.21 us (kalman adjust)
Setting multicast TTL to 32
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 3] local 192.168.1.1 port 49710 connected with 224.0.55.55 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 3] 0.0- 1.0 sec 131 KBytes 1.07 Mbits/sec
[ 3] 1.0- 2.0 sec 128 KBytes 1.05 Mbits/sec
[ 3] 2.0- 3.0 sec 128 KBytes 1.05 Mbits/sec
[ 3] 0.0- 3.0 sec 386 KBytes 1.05 Mbits/sec
[ 3] Sent 269 datagrams
root@localhost:~#
The excerpt below shows the log of each device after running tcpdump to log the traffic on each interface:
Device1:
root@localhost:~# tcpdump
[16969.941780] device enp0s4 entered promiscuous mode
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on enp0s4, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
13:30:55.877791 IP 192.168.1.1.37631 > 224.0.55.55.5001: UDP, length 1470
13:30:55.890941 IP 192.168.1.1.37631 > 224.0.55.55.5001: UDP, length 1470
...
13:33:48.716221 IP 192.168.1.1.35653 > 224.0.55.55.5001: UDP, length 1470
Device2:
root@localhost:~# tcpdump
[17022.680227] device enp0s4 entered promiscuous mode
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on enp0s4, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
Device3:
root@localhost:~# tcpdump
[17077.051525] device enp0s4 entered promiscuous mode
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on enp0s4, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
13:32:54.377608 IP 192.168.1.1.57427 > 224.0.55.55.5001: UDP, length 1470
13:32:54.386654 IP 192.168.1.1.57427 > 224.0.55.55.5001: UDP, length 1470
...
13:32:55.411938 IP 192.168.1.1.57427 > 224.0.55.55.5001: UDP, length 1470
Based on the above, we can see that the multicast traffic was only forwarded to Device1 and Device3 successfully.
NOTE: The above was tested on a virtual machine